So you’ve got a dental infection, huh? Well, let’s not waste any time – managing this situation is crucial. You see, dental infections, like oral cellulitis, are no joke and can even become life-threatening if left untreated. But fear not, because your dentist is here to save the day. They can prescribe antibiotics and other treatments to effectively manage and resolve the infection. So let’s get you on the path to a healthy and infection-free mouth!
Understanding Dental Infections
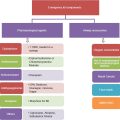
Dental infections can be a concerning and potentially serious issue if not properly addressed. These infections can occur due to a variety of reasons, resulting in discomfort, pain, and even life-threatening complications. It is important to understand the causes, signs, and complications of dental infections in order to effectively diagnose, treat, and prevent these issues from arising.
Causes of Dental Infections
Dental infections can be caused by a range of factors, with poor oral hygiene being a common contributor. When proper oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, are neglected, bacteria can build up in the mouth and lead to infections. Other potential causes include tooth decay, gum disease, dental trauma, and dental procedures such as root canals or tooth extractions.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of dental infections is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common symptoms include toothache, sensitivity to temperature or pressure, swelling and redness in the gums or face, bad breath, and a foul taste in the mouth. In some cases, individuals may also experience fever, difficulty swallowing, or swollen lymph nodes. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to seek dental care promptly.
Complications of Dental Infections
While dental infections may initially seem like a minor issue, they can lead to serious complications if left untreated. These complications can include the spread of infection to other parts of the body, abscess formation, damage to surrounding tissues or bone, and even systemic infections that can be life-threatening. It is crucial to address dental infections promptly to avoid these potential complications.
Diagnosing Dental Infections
Proper diagnosis is essential for effective treatment of dental infections. Dentists employ various methods to diagnose these infections, including patient history and examination, diagnostic imaging techniques, and microbiological analysis.
Patient History and Examination
During the initial examination, the dentist will gather information about the patient’s medical and dental history. This includes asking about symptoms, any previous dental procedures or infections, and any underlying health conditions. The dentist will then perform a thorough examination of the teeth, gums, and surrounding tissues to assess the presence and extent of the infection.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
To further evaluate dental infections, dentists may utilize diagnostic imaging techniques such as X-rays or CT scans. These imaging methods provide detailed images of the teeth, roots, and surrounding structures, allowing the dentist to identify any underlying issues, such as abscesses or bone loss, that may be contributing to the infection.
Microbiological Analysis
In some cases, dentists may also perform microbiological analysis to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection. This analysis involves taking a sample from the infected area and sending it to a laboratory for testing. The results of this analysis can help guide the dentist in determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
Treatment Options for Dental Infections
Once diagnosed, dental infections can be treated using various methods. The treatment option recommended by the dentist will depend on the severity of the infection and individual factors.
Antibiotics for Dental Infections
Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat dental infections, especially in cases of severe or systemic infections. These medications work by killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria responsible for the infection. It is important to take antibiotics as prescribed and for the entire duration of the treatment to ensure the infection is eradicated completely.
Drainage and Irrigation Procedures
In some cases, the dentist may need to perform drainage and irrigation procedures to remove pus or fluid from an abscessed area or infected tooth. This helps alleviate pain, reduce swelling, and promote healing. The dentist will carefully clean and irrigate the affected area to remove bacteria and debris and may place a temporary drain to aid in the healing process.
Root Canal Therapy
Root canal therapy may be necessary when dental infections involve the pulp of the tooth. This procedure involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning the root canals, and sealing them to prevent reinfection. Root canal therapy can effectively treat dental infections while preserving the natural tooth structure.
Tooth Extraction
In cases where the infected tooth cannot be saved or poses a risk to surrounding teeth and tissues, tooth extraction may be necessary. The dentist will carefully remove the infected tooth and may prescribe antibiotics to prevent further infection. Following extraction, the dentist will discuss options for replacing the missing tooth, such as dental implants or bridges.
Preventive Measures for Dental Infections
Taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing dental infections. By maintaining good oral hygiene, attending regular dental check-ups, and considering vaccinations for oral health, individuals can protect themselves from these potentially serious issues.
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene
Practicing good oral hygiene is essential for preventing dental infections. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using mouthwash or antiseptic rinses to reduce bacteria in the mouth. Additionally, individuals should avoid tobacco use and limit their intake of sugary foods and drinks, as these can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
Regular dental check-ups are crucial for detecting and preventing dental infections. Dentists can identify early signs of infection or underlying issues during routine dental exams. They can also provide professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar that cannot be effectively removed through regular brushing and flossing.
Vaccinations for Oral Health
In recent years, vaccinations for certain oral infections, such as human papillomavirus (HPV), have become available. These vaccinations can help reduce the risk of developing infections that can lead to oral cancers. It is important to discuss vaccination options with your dentist or healthcare provider to determine if they are appropriate for you.
Managing Specific Dental Infections
Certain types of dental infections may require specific management approaches. These include managing dental abscesses, periodontal infections, dental infections in children, and dental infections in elderly patients.
Managing Dental Abscesses
Dental abscesses are pockets of pus that form in the teeth or gums and are often accompanied by severe pain and swelling. Treatment typically involves draining the abscess, prescribing antibiotics to eliminate infection, and addressing the underlying cause, such as tooth decay or gum disease. Root canal therapy or tooth extraction may be necessary to fully treat the infection.
Managing Periodontal Infections
Periodontal infections, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, affect the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. Treatment options may include scaling and root planing to remove bacteria and plaque from the gum line, professional cleanings, and use of antimicrobial agents. In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary.
Managing Dental Infections in Children
Children may be more susceptible to dental infections due to their developing immune systems and oral hygiene habits. Prevention, such as proper oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups, is key to managing and preventing infections in children. Early intervention and treatment are crucial to prevent the spread of infection and maintain oral health.
Managing Dental Infections in Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals may face unique challenges when it comes to dental infection management. Age-related factors, such as dry mouth and weakened immune systems, can make them more susceptible to infections. Regular dental check-ups, maintaining good oral hygiene, and prompt treatment of any potential infections are essential for managing oral health in elderly patients.
View all our emergency dental services
Guidelines for Dental Infection Control
Proper infection control protocols are vital in dental settings to prevent the spread of infections. Dentists and dental staff must adhere to guidelines for personal protective equipment (PPE), sterilization and disinfection protocols, and safe handling and disposal of infectious materials.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Dental professionals must wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, masks, and protective eyewear, to minimize the risk of exposure to infectious agents. This helps protect both the healthcare provider and the patient.
Sterilization and Disinfection Protocols
Proper sterilization and disinfection protocols must be followed for dental instruments and equipment. This includes thorough cleaning, sterilization of reusable instruments, and appropriate use of disinfectants on surfaces and dental unit waterlines.
Safe Handling and Disposal of Infectious Materials
Dental practices must have protocols in place for the safe handling and disposal of infectious materials, such as contaminated sharps and extracted teeth. These materials should be disposed of according to regulations and guidelines to prevent the spread of infections.
Complications and Side Effects of Dental Infection Management
While managing dental infections is essential for oral health, there can be potential complications and side effects associated with treatment.
Allergic Reactions to Antibiotics
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to antibiotics used in the treatment of dental infections. These reactions can range from mild rashes to severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis. It is important to inform your dentist about any known allergies or adverse reactions to medications before starting treatment.
Resistant Bacterial Infections
In certain cases, bacteria causing dental infections may be resistant to certain antibiotics. This can make it more challenging to effectively treat the infection. Dentists may need to adjust the treatment approach or prescribe alternative antibiotics to address resistant infections.
Pain and Discomfort After Treatment
Following treatment for dental infections, it is common to experience some pain and discomfort. This can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers as recommended by your dentist. However, if the pain persists or worsens, it is important to seek further dental care.
Complications of Surgical Procedures
Certain dental infections may require surgical procedures, such as tooth extractions or periodontal surgeries. While these procedures are generally safe, there can be potential complications such as bleeding, infection, or damage to surrounding structures. Proper post-operative care and following the dentist’s instructions can help minimize these risks.
Alternative and Adjunctive Therapies for Dental Infections
In addition to conventional treatments, some individuals may seek alternative or adjunctive therapies for dental infections. These therapies, while not widely supported by scientific evidence, may offer additional relief or support in conjunction with traditional treatments.
Herbal Remedies and Natural Products
Some individuals may explore the use of herbal remedies and natural products as complementary therapies for dental infections. Examples include using tea tree oil, garlic, or clove oil for their antibacterial or pain-relieving properties. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using these remedies to ensure their safety and efficacy.
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) involves the use of light-activated photosensitizers to target and kill bacteria. This therapy may be used as an adjunct to conventional treatment for dental infections. PDT has shown promising results in reducing bacterial load and promoting healing.
Laser Treatment
Laser therapy is another adjunctive treatment option that may be used for dental infections. Dental lasers can be used to remove infected tissue, promote healing, and reduce bacterial load. However, the efficacy of laser treatment for dental infections is still being studied, and further research is needed.
Special Considerations for Immunocompromised Patients
Immunocompromised patients, such as those with HIV/AIDS, organ transplant recipients, or undergoing cancer treatment, require special considerations when managing dental infections. These individuals may be more susceptible to infections and may require additional precautions and tailored treatment approaches.
Dental Infections in HIV/AIDS Patients
Dental infections can pose significant risks for individuals living with HIV/AIDS. These patients may experience more severe infections, slower healing, and a higher risk of complications. Dentists treating HIV/AIDS patients must carefully consider the patient’s immune status, potential drug interactions, and overall healthcare needs.
Precautions for Organ Transplant Recipients
Organ transplant recipients often require long-term immunosuppressive medication, which can increase the risk of infections. Dental infections can have serious consequences for these patients, and dentists must coordinate with the patient’s transplant team to ensure appropriate management and minimize infection-related risks.
Managing Dental Infections in Cancer Patients
Cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy or chemotherapy may be at a heightened risk of dental infections due to compromised immune systems and increased susceptibility to oral complications. Dentists working with cancer patients must consider the potential side effects of cancer treatments and adjust dental care accordingly.
The Role of Proper Oral Hygiene in Combating Dental Infections
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices is crucial for preventing dental infections. By incorporating effective brushing techniques, dental flossing, using mouthwashes and antiseptic rinses, and utilizing interdental cleaning devices, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing infections.
Brushing Techniques and Dental Flossing
Proper brushing techniques, including using a soft-bristled toothbrush and brushing for at least two minutes, can help remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gums. Flossing daily also plays a crucial role in cleaning areas between the teeth where a toothbrush cannot reach.
Mouthwashes and Antiseptic Rinses
Mouthwashes and antiseptic rinses can complement brushing and flossing by reducing the bacterial load in the mouth. These products can help kill bacteria and freshen breath. It is important to choose mouthwashes and rinses that are recommended by dental professionals and follow the instructions for use.
Interdental Cleaning Devices
Interdental cleaning devices, such as interdental brushes or water flossers, can be used to clean between the teeth and remove bacteria and debris. These devices may be particularly useful for individuals with braces, dental implants, or gaps between teeth where traditional flossing may be challenging.
In conclusion, dental infections should never be taken lightly, as they can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Understanding the causes, signs, and potential complications of dental infections is essential for prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By maintaining good oral hygiene practices, attending regular dental check-ups, and following the guidelines for infection control, individuals can reduce the risk of dental infections and protect their oral health. Remember, early intervention and proper management are key to preventing further issues and maintaining a healthy smile.