You’ve probably experienced the discomfort of a gum abscess before – that painful swelling that makes it difficult to eat or speak. But fear not, because there is an effective treatment available that can provide you with much-needed relief. By visiting a dentist, they can not only drain the abscess but also tackle the root cause of the problem – gum disease. So, if you find yourself dealing with a gum abscess, don’t delay seeking the necessary treatment to restore your oral health.
Treatment for Gum Abscess
Having a gum abscess can be a painful and uncomfortable experience. However, the good news is that there are various treatment options available to alleviate the symptoms and address the underlying causes. In this article, we will discuss the overview, causes, signs, and symptoms of a gum abscess, as well as the different treatment options and preventive measures you can take.
Overview of Gum Abscess
A gum abscess, also known as a periodontal abscess, is a localized collection of pus that forms within the gum tissues. It is often caused by an infection in the pockets surrounding the teeth, which are usually a result of poor oral hygiene or gum disease. If left untreated, a gum abscess can lead to more severe complications, such as bone loss or the spread of infection to other parts of the body.
Causes of Gum Abscess
The primary cause of a gum abscess is the presence of bacteria in the gum pockets. These bacteria can enter the gum tissues through small openings or cuts and multiply, leading to an infection. Poor oral hygiene, such as inadequate brushing and flossing, can contribute to the buildup of plaque and tartar, which provide a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria. Other factors that may increase the risk of developing a gum abscess include smoking, a weakened immune system, and certain medical conditions like diabetes.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Abscess
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a gum abscess is crucial to seek timely treatment. Common signs of a gum abscess include:
- Persistent and throbbing toothache
- Swelling and redness in the gum tissues
- A foul taste or odor in the mouth
- Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures
- Difficulty chewing and biting
- Pus discharge from the affected area
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck or jaw
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a dentist as soon as possible to prevent further complications.
Diagnosis of Gum Abscess
To diagnose a gum abscess, a dentist will perform a thorough examination of your oral cavity. They will check for any swelling, redness, or discharge in the gum tissues, as well as evaluate the teeth for signs of decay or infection. In some cases, dental X-rays may be recommended to assess the extent of the infection and determine if there is any underlying bone damage or abscess formation.
Immediate Home Remedies for Gum Abscess
While seeking professional dental treatment is essential for effectively treating a gum abscess, there are some immediate home remedies that can help provide temporary relief until your dental appointment. These remedies can include:
- Rinsing your mouth with warm saltwater to reduce inflammation and soothe the affected area.
- Applying a cold compress to the outside of your cheek to alleviate pain and swelling.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help manage the discomfort.
However, it is important to note that these home remedies are not a substitute for professional dental care, and you should still schedule an appointment with your dentist to address the underlying cause of the gum abscess.
View all our emergency dental services
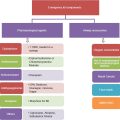
Professional Dental Treatment for Gum Abscess
When it comes to treating a gum abscess, professional dental care is crucial. Your dentist may recommend one or more treatment options depending on the severity of the abscess and the underlying gum disease.
1. Drainage of Gum Abscess
To relieve the pressure and remove the accumulated pus, the dentist may perform a drainage procedure. There are several methods for draining a gum abscess, including:
1.1. Incision and Drainage
In this procedure, the dentist will make a small incision in the gum tissue to allow the pus to drain out. Once the abscess is drained, they may clean the area and prescribe antibiotics to control the infection.
1.2. Root Canal Treatment
If the abscess is associated with an infected tooth, a root canal treatment may be necessary. This involves removing the infected pulp from the tooth and sealing it to prevent further infection.
1.3. Periodontal Surgery
In more severe cases, periodontal surgery may be required to treat the gum abscess. This procedure involves accessing the infected gum pockets, removing the bacteria and diseased tissue, and repositioning the gums to promote healing and prevent future abscess formation.
1.4. Gum Pocket Cleaning
Another treatment option is a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing. This involves removing the plaque and tartar buildup from the gum pockets and smoothing the tooth roots to prevent further bacterial growth.
2. Resolution of Underlying Gum Disease
Treating the underlying gum disease is vital to prevent the recurrence of a gum abscess. Some treatment options for gum disease management include:
2.1. Scaling and Root Planing
This procedure, also known as a deep cleaning, involves the removal of plaque and tartar from the teeth and roots. It helps to eliminate the bacteria responsible for gum disease and promotes gum healing.
2.2. Antibiotic Therapy
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to control the infection and reduce inflammation. These medications can be taken orally or applied topically to the affected areas.
2.3. Antimicrobial Mouthwashes
To maintain good oral hygiene and control bacterial growth, your dentist may suggest using antimicrobial mouthwashes. These mouthwashes contain ingredients that help kill the bacteria present in the gum pockets.
2.4. Dental Restorations
If the gum abscess and gum disease have caused significant damage to the teeth, your dentist may recommend dental restorations such as fillings, crowns, or even tooth extraction and replacement options like dental implants or bridges.
Recovery and Aftercare for Gum Abscess
After undergoing treatment for a gum abscess, it is crucial to follow the dentist’s instructions for proper recovery and aftercare. This may include:
- Taking any prescribed medications, such as antibiotics or pain relievers, as instructed.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly.
- Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and being gentle while brushing the treated area.
- Avoiding smoking or tobacco use, as it can hinder the healing process and increase the risk of complications.
- Scheduling regular dental check-ups and cleanings to monitor the healing process and prevent future abscesses.
Prevention of Gum Abscess
Preventing gum abscesses starts with maintaining good oral hygiene practices. Make sure to brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, floss daily, and rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings can also help identify and treat early signs of gum disease, preventing the formation of abscesses.
When to See a Dentist for Gum Abscess
If you suspect you have a gum abscess or are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned earlier, it is essential to see a dentist promptly. Delaying treatment can lead to more severe complications and potential damage to your oral health. So, don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment and discuss your concerns with a dental professional who can provide the appropriate diagnosis and treatment for your gum abscess. Remember, early intervention is key to a successful recovery and the preservation of your oral health.