Have you ever experienced excruciating pain and swelling in your mouth? Chances are, you might be dealing with a dental abscess. Dental abscesses are painful infections that can occur around the root of a tooth or in the gums. In order to provide relief and prevent further complications, dentists are able to drain the abscess and prescribe antibiotics if necessary. Understanding dental abscess drainage is essential for anyone who wants to alleviate the discomfort and protect their oral health.
What is a Dental Abscess?
A dental abscess is a painful infection that can form around the root of a tooth or in the gums. It typically occurs due to bacterial infection, which can occur as a result of tooth decay, gum disease, or trauma to the tooth. The abscess forms as a pocket of pus, and if left untreated, it can cause further complications and spread the infection to other areas of the mouth or body.
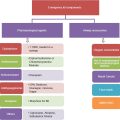
Types of Dental Abscess
There are three main types of dental abscess: periapical abscess, periodontal abscess, and gingival abscess.
Periapical Abscess
A periapical abscess is the most common type of dental abscess and it occurs at the tip of the tooth’s root. It usually develops as a result of an untreated dental cavity or tooth decay. If the infection spreads to the root canal, it can cause a periapical abscess.
Periodontal Abscess
A periodontal abscess occurs in the gums, specifically in the space between the tooth and the gum tissue. It typically arises from an infection in the gum pockets caused by gum disease or poor oral hygiene. This type of abscess can also form as a result of food particles getting stuck in the gum pockets, leading to infection and inflammation.
Gingival Abscess
A gingival abscess is a localized infection that occurs in the gum tissue itself, rather than in the tooth or bone. It is commonly caused by trauma to the gums, such as biting down on a hard object or aggressive tooth brushing. Poor oral hygiene and certain dental treatments that cause gum irritation can also contribute to the development of a gingival abscess.
Symptoms of Dental Abscess
The symptoms of a dental abscess can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Severe and persistent toothache
- Swelling and redness in the affected area
- Sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures
- Pain when chewing or biting down
- Bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth
- Inflamed and swollen lymph nodes in the neck and jaw area
- Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing due to swelling
- Pus or drainage from the infected area
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek prompt dental treatment to prevent further complications.
Complications of Dental Abscess
If left untreated, a dental abscess can lead to various complications that can have serious consequences for your oral and overall health. Some of these complications include:
Spread of Infection
One of the primary risks of an untreated dental abscess is the spread of infection. The infection can extend from the tooth or gum tissue to the surrounding bones, causing osteomyelitis, a potentially serious bone infection. Additionally, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the sinuses, jaw, or even the brain, leading to more severe health issues.
Bone Loss
Untreated dental abscesses can cause bone loss in the jaw, which can weaken the foundation of the teeth and eventually lead to tooth loss. The infection can erode the bone tissue, affecting the stability and alignment of the surrounding teeth.
Systemic Infection
In rare cases, a dental abscess can lead to a systemic infection, known as sepsis. Sepsis is a life-threatening condition characterized by the body’s inflammatory response to an infection. It can cause organ failure, septic shock, and even death if not treated promptly.
Diagnosing a Dental Abscess
In order to accurately diagnose a dental abscess, your dentist will conduct a thorough examination and may require additional tests. The diagnostic process typically involves the following:
Physical Examination
During the physical examination, your dentist will inspect the affected area, looking for signs of swelling, redness, or drainage. They will also evaluate the extent of pain and tenderness to determine the location and severity of the abscess.
X-rays and Imaging
X-rays may be taken to identify the abscess and assess any potential damage to the tooth or bone. In some cases, your dentist may recommend additional imaging techniques, such as a CT scan or ultrasound, to obtain a more detailed view of the infection.
Evaluation of Symptoms
Your dentist will inquire about your symptoms, including the duration and intensity of the pain, any accompanying symptoms, and your dental and medical history. This information will help in determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for a dental abscess may vary depending on the severity and type of abscess, as well as your overall oral health. Some common treatment approaches include:
Drainage of the Abscess
In order to alleviate the pain and eliminate the source of infection, your dentist may perform an abscess drainage procedure. This involves making an incision into the abscess to allow the pus to drain out. Drainage can provide immediate relief and help speed up the healing process.
Prescription of Antibiotics
In addition to drainage, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help combat the infection. Antibiotics can help eradicate the bacteria causing the abscess and prevent the infection from spreading. It is important to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed and follow your dentist’s instructions.
Root Canal Treatment
If the abscess is associated with a dead or severely infected tooth, root canal treatment may be necessary. This procedure involves removing the infected tissue from the tooth’s root canal, disinfecting the area, and sealing it to prevent reinfection.
Tooth Extraction
In cases where the tooth is severely damaged or cannot be saved, extraction may be the best option. Tooth extraction removes the source of infection and prevents the spread of bacteria to other areas. Your dentist will discuss the possibility of tooth replacement options, such as dental implants or bridges, to restore the aesthetics and function of your smile.
View all our emergency dental services
Understanding Dental Abscess Drainage
Dental abscess drainage is a procedure performed by dentists to remove the pus and infection from the abscessed area. Drainage is an essential step in the treatment of a dental abscess, as it helps alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and promote healing.
Purpose of Drainage
The main purpose of dental abscess drainage is to eliminate the source of infection. By draining the abscess, the buildup of pus and bacteria is removed, relieving pressure and pain. Drainage also allows for better access to the infected area and promotes faster healing.
Drainage Techniques
There are different techniques that can be used to perform a dental abscess drainage procedure, depending on the location and size of the abscess. Incision and drainage is one of the most common methods, where the dentist makes a small incision to release the pus and facilitate drainage. Alternatively, a needle may be used to aspirate the pus from the abscess.
Local Anesthesia
Before the drainage procedure, your dentist will administer local anesthesia to numb the area and minimize any discomfort or pain during the procedure. This ensures that you can undergo the drainage procedure comfortably.
Preparing for Dental Abscess Drainage
To ensure a successful dental abscess drainage procedure, certain preparations should be made. These preparations involve providing your dentist with relevant medical history and following pre-procedure instructions.
Medical History
Before the drainage procedure, it is important to inform your dentist about any medical conditions, allergies, or medications you are currently taking. This will help your dentist determine the most appropriate approach and make any necessary adjustments to the procedure.
Pre-procedure Instructions
Your dentist will provide you with specific pre-procedure instructions to follow before the dental abscess drainage. These instructions may include restrictions on eating or drinking prior to the procedure and advice on any medications that need to be discontinued temporarily. It is crucial to adhere to these instructions to ensure a successful drainage procedure.
Possible Risks and Complications
Your dentist will discuss the potential risks and complications associated with the drainage procedure. Although it is a relatively safe procedure, there is a slight risk of bleeding, infection, or damage to surrounding structures. Understanding these risks will help you make an informed decision and alleviate any concerns you may have.
The Dental Abscess Drainage Procedure
The dental abscess drainage procedure typically involves several steps, including anesthetic administration, incision and drainage technique, and wound cleaning and dressing.
Anesthetic Administration
To ensure your comfort and minimize pain during the procedure, your dentist will first administer local anesthesia. This is done by injecting an anesthetic agent into the area around the abscess. The anesthesia will numb the area, allowing the dentist to perform the drainage without discomfort.
Incision and Drainage Technique
Once the area is numb, your dentist will make a small incision into the abscess using a scalpel or needle. This incision allows for the release of pus and facilitates proper drainage. The dentist will gently squeeze the area to encourage the removal of pus and debris. In some cases, a small drain may be inserted to aid in the drainage process.
Cleaning and Dressing the Wound
After the drainage is complete, your dentist will thoroughly clean the abscess cavity to remove any remaining bacteria or debris. This is typically done using a saline solution or a mild antiseptic. Once the area is clean, a sterile gauze or dressing may be placed over the wound to protect it and promote further healing.
Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
After the dental abscess drainage procedure, it is important to follow post-procedure care instructions to promote healing and prevent complications.
Pain Management
Some discomfort or soreness in the treated area is normal after the drainage procedure. Your dentist may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, to help manage any pain or swelling. It is important to avoid aspirin, as it can increase the risk of bleeding.
Antibiotic Regimen
Depending on the severity of the infection and the dentist’s recommendation, you may be prescribed antibiotics after the drainage procedure. It is important to take the full course of antibiotics as directed, even if the symptoms improve, in order to fully eradicate the infection.
Follow-up Appointments
Your dentist will schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your progress and ensure proper healing. During these visits, the dentist will evaluate the wound, remove any drainage tubes if necessary, and make any further recommendations for ongoing care.
Avoiding Dental Abscess Recurrence
To prevent the recurrence of a dental abscess, proper oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups are crucial.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential in preventing dental abscesses. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily to remove plaque and food debris from between your teeth, and using an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria. Additionally, it is important to avoid excessive consumption of sugary foods and drinks, as they can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are essential for early detection and prevention of dental abscesses. During these visits, your dentist can thoroughly examine your teeth and gums, identify any signs of infection or decay, and provide necessary treatments to prevent the development of abscesses.
By following these preventive measures and seeking prompt dental treatment when necessary, you can significantly reduce the risk of dental abscesses and maintain optimal oral health. Remember, prevention is always better than cure when it comes to dental abscesses.